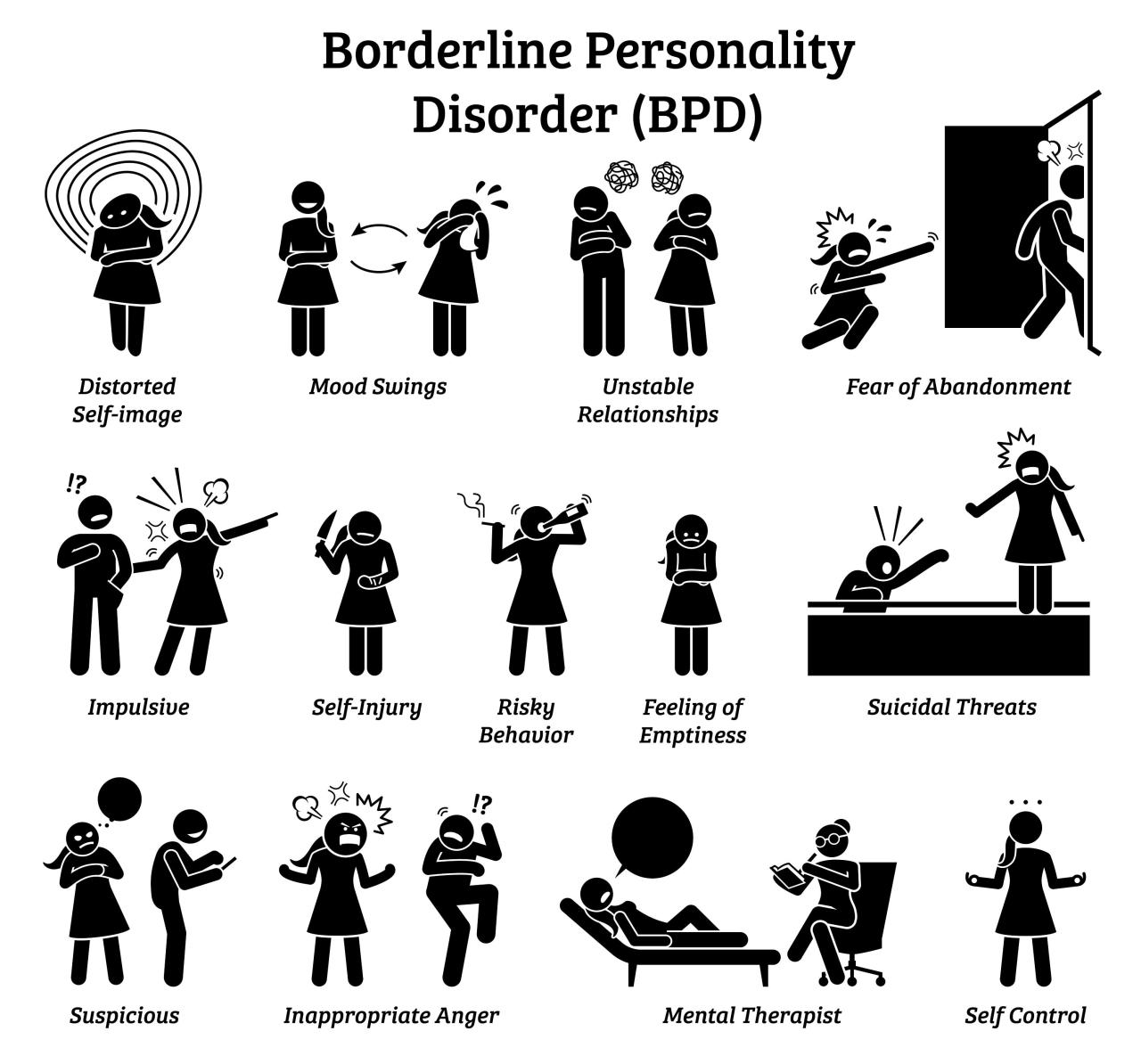
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a complex mental health condition that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It is characterized by intense emotions, unstable relationships, and impulsive behaviors. Understanding BPD is crucial for individuals seeking support and for those who care about them.
This comprehensive guide delves into the key characteristics and symptoms of BPD, explores the prevalence and risk factors associated with it, and provides examples of how it manifests in individuals’ lives. Additionally, it discusses the various treatment options available, including Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) and Schema Therapy, and their effectiveness in managing BPD symptoms.
Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
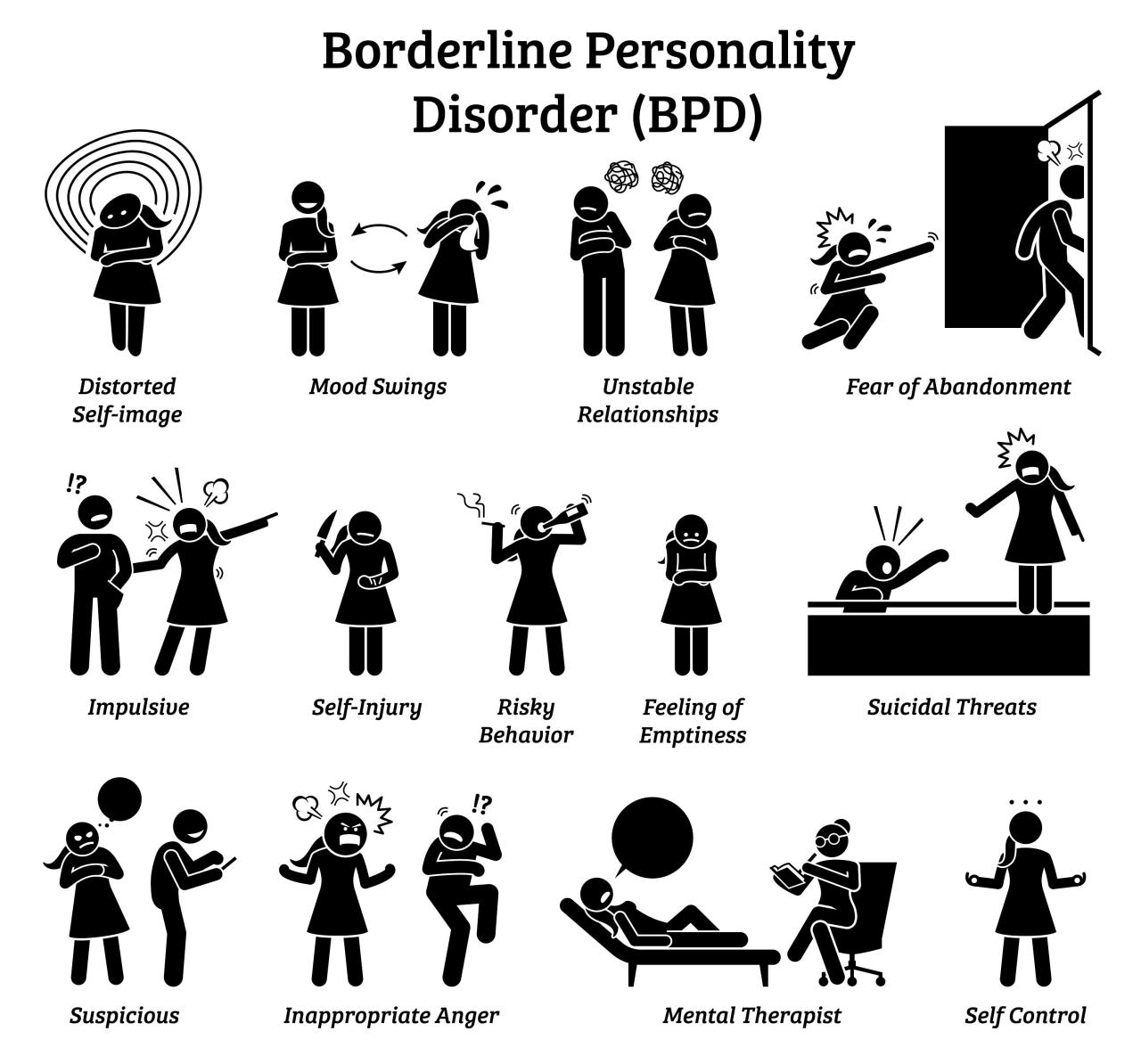
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a complex mental health condition that affects an individual’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. It is characterized by a pattern of intense and unstable relationships, emotional dysregulation, and impulsive behavior. Understanding BPD is crucial for providing effective support and treatment to individuals who are affected by it.
Key Characteristics and Symptoms of BPD, Borderline personality disorder
BPD is diagnosed based on specific criteria Artikeld in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). These criteria include:
- A pattern of unstable and intense interpersonal relationships, characterized by alternating between idealization and devaluation.
- Impulsive behavior in at least two areas, such as spending, substance use, or unsafe sex.
- Marked mood swings that last for a few hours to a few days.
- Chronic feelings of emptiness.
- Inappropriate, intense anger or difficulty controlling anger.
- Recurrent suicidal behavior, gestures, or threats.
- Transient, stress-related paranoid ideation or severe dissociative symptoms.
Prevalence and Risk Factors Associated with BPD
BPD affects approximately 1.6% of the general population and is more common in women than men. The exact cause of BPD is unknown, but it is thought to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
Risk factors associated with BPD include:
- Family history of BPD or other mental health disorders.
- Childhood trauma or abuse.
- Exposure to chronic stress.
- Certain personality traits, such as impulsivity and emotional instability.
Examples of How BPD Affects Individuals’ Thoughts, Emotions, and Behaviors
BPD can significantly impact an individual’s life, affecting their relationships, work, and overall well-being. Here are some examples of how BPD can manifest in individuals:
- Thoughts:Individuals with BPD may experience intense and rapidly shifting thoughts, including thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
- Emotions:They may experience extreme mood swings, from intense happiness to overwhelming sadness or anger.
- Behaviors:Impulsive behaviors, such as self-harm, substance abuse, or risky sexual behavior, are common in BPD.
Treatment Options for BPD
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a complex mental illness that can cause significant distress and impairment in various aspects of life. Treatment for BPD typically involves a combination of psychotherapy and medication, with the primary goal of improving emotional regulation, interpersonal functioning, and overall well-being.
There are several therapeutic approaches that have been found to be effective in treating BPD, including:
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
DBT is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy that was specifically developed for treating BPD. It focuses on helping individuals develop skills in four key areas:
- Mindfulness: Paying attention to the present moment without judgment.
- Interpersonal effectiveness: Communicating and interacting with others in a healthy way.
- Emotion regulation: Managing and controlling emotions in a healthy way.
- Distress tolerance: Coping with and tolerating distress without resorting to unhealthy behaviors.
DBT has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of BPD, including emotional instability, self-harm, and suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Schema Therapy
Schema therapy is a type of psychotherapy that focuses on identifying and changing maladaptive schemas, or patterns of thinking and behavior, that contribute to BPD symptoms.
Schema therapy has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of BPD, including emotional instability, interpersonal problems, and self-harm.
| Treatment Modality | Key Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) | Focuses on developing skills in mindfulness, interpersonal effectiveness, emotion regulation, and distress tolerance. | Reduces symptoms of BPD, including emotional instability, self-harm, and suicidal thoughts and behaviors. |
| Schema Therapy | Focuses on identifying and changing maladaptive schemas, or patterns of thinking and behavior, that contribute to BPD symptoms. | Reduces symptoms of BPD, including emotional instability, interpersonal problems, and self-harm. |
The choice of treatment for BPD will depend on the individual’s specific needs and preferences. It is important to work with a mental health professional to determine the best course of treatment.
Impact of BPD on Relationships and Social Functioning: Borderline Personality Disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD) can have a significant impact on relationships and social functioning. Individuals with BPD often struggle to maintain stable and fulfilling relationships due to difficulties regulating their emotions, managing interpersonal boundaries, and engaging in healthy communication.
Challenges in Relationships
- Intense and Unstable Relationships:Individuals with BPD may experience intense and unstable relationships characterized by extreme idealization and devaluation of others. They may swing between idealizing their partners as perfect and devaluing them as worthless, leading to emotional rollercoasters.
- Difficulty Managing Emotions:Emotional dysregulation is a hallmark of BPD. Individuals with BPD may experience intense and overwhelming emotions that can make it challenging for them to regulate their behavior in relationships. They may have difficulty controlling their anger, sadness, or fear, which can lead to conflicts and misunderstandings.
- Boundary Issues:Individuals with BPD often struggle with boundary setting and maintaining. They may have difficulty respecting the boundaries of others and may become overly dependent or clingy. Conversely, they may push others away due to feelings of abandonment or rejection.
- Communication Difficulties:Communication can be challenging for individuals with BPD. They may have difficulty expressing their needs and feelings clearly and may resort to manipulative or passive-aggressive behaviors. They may also be sensitive to criticism or perceived rejection, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts.
Strategies for Improving Relationships
Despite the challenges, it is possible for individuals with BPD to build and maintain healthy relationships. Here are some strategies:
- Seek Professional Help:Therapy can provide individuals with BPD with the skills and support they need to manage their symptoms and improve their relationships. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) are two evidence-based therapies that have been shown to be effective for BPD.
- Improve Communication:Individuals with BPD can benefit from learning effective communication skills. They can practice expressing their needs and feelings clearly, using “I” statements, and listening attentively to others.
- Set Boundaries:Establishing and maintaining clear boundaries is essential for healthy relationships. Individuals with BPD can work with their therapist to identify and set appropriate boundaries with others.
- Practice Mindfulness:Mindfulness techniques can help individuals with BPD become more aware of their emotions and behaviors. By practicing mindfulness, they can learn to regulate their emotions and respond to situations in a more balanced and healthy way.
Closing Summary
Borderline personality disorder can significantly impact relationships and social functioning, presenting challenges in maintaining stable connections with family, friends, and romantic partners. However, with the right support and strategies, individuals with BPD can learn to manage their emotions, improve communication, and build healthy relationships.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of BPD, empowering individuals to seek the necessary help and support they need to navigate this complex condition and live fulfilling lives.
FAQ
What are the key characteristics of BPD?
Key characteristics include intense emotions, unstable relationships, impulsive behaviors, fear of abandonment, and self-harm.
What are the risk factors for developing BPD?
Risk factors include genetics, childhood trauma, and certain personality traits.
How is BPD treated?
Treatment options include psychotherapy, such as Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) and Schema Therapy, as well as medication.